C. George Boeree, PhD
Psychology Department
Shippensburg University
© Copyright C. George Boeree 2009
Instinct
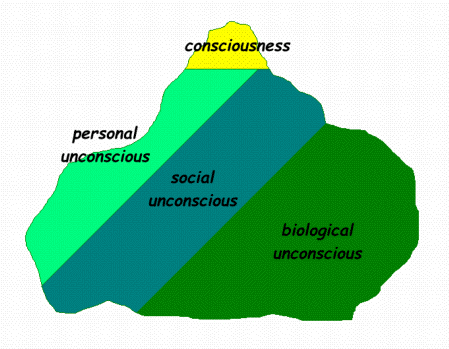
The archetype has no form of its own, but it acts as an
"organizing
principle" on the things we see or do. It works the way that instincts
work in Freud's theory: At first, the baby just wants something to eat,
without knowing what it wants. It has a rather indefinite yearning
which,
nevertheless, can be satisfied by some things and not by others. Later,
with experience, the child begins to yearn for something more specific
when it is hungry -- a bottle, a cookie, a broiled lobster, a slice of
New York style pizza. The archetype is like a black hole in
space: You only know its there
by how it draws matter and light to itself.
The mother archetype is a
particularly good example. All of our ancestors had mothers. We have
evolved in an environment that included a mother or mother-substitute.
We would never have survived without our connection with a
nurturing-one during our times as helpless infants. It stands to reason
that we are "built" in a way that reflects that evolutionary
environment: We come into this world ready to want mother, to seek her,
to recognize her, to deal with her. The mother archetype is symbolized
by the primordial mother or "earth mother" of mythology, by Eve and
Mary in western traditions, and by less personal symbols such as the
church, the nation, a forest, or the ocean.
Besides mother, their are other family archetypes. Obviously, there is father, who is often symbolized by
a guide or an authority figure. There is also the archetype family, which represents the idea
of blood relationship and ties that run deeper than those based on
conscious reasons.
There is also the child,
represented in mythology and art by children, infants most especially,
as well as other small creatures. The Christ child celebrated at
Christmas is a manifestation of the child archetype, and represents the
future, becoming, rebirth, and salvation. Curiously, Christmas falls
during the winter solstice, which in northern primitive cultures also
represents the future and rebirth. People used to light bonfires and
perform ceremonies to encourage the sun's return to them. The child
archetype often blends with other archetypes to form the child-god, or
the child-hero.
In Jung's theory, instincts involving simple survival and reproduction are a part of an archetype called the shadow. He believed that it derives from our prehuman, animal past, when our concerns were limited to survival and reproduction, and when we weren't self-conscious.
Jung believed that we often turn it into the "dark side" of our personalities, and the evil that we are capable of is often stored there in the form of a complex. Actually, the shadow is amoral -- neither good nor bad, just like animals. An animal is capable of tender care for its young and vicious killing for food, but it doesn't choose to do either. It just does what it does. It is "innocent." But from our human perspective, the animal world looks rather brutal, inhuman, so the shadow becomes something of a garbage can for the parts of ourselves that we can't quite admit to.
Symbols of the shadow include the snake (as in the garden of Eden), the dragon, monsters, and demons. It often guards the entrance to a cave or a pool of water, which is the collective unconscious. Next time you dream about wrestling with the devil, it may only be yourself you are wrestling with!
There are also, of course, instincts relating to the interaction of
the sexes. Jung postulated two archetypes: The anima is the female
aspect present in men, and the animus
is the
male aspect present in women. In myths and, Jung believed, dreams, the
anima may be personified as a young girl, very spontaneous and
intuitive,
or as a witch, or as the earth mother. It is likely to be associated
with
deep emotionality and the force of life itself. The animus may be
personified
as a wise old man, a sorcerer, or often a number of males, and tends to
be logical, often rationalistic, even argumentative.
Jung also has an archetype called the hermaphrodite. An hermaphrodite is
both
male and female,
and so represents
the
union
of opposites, an important idea in Jung's theory. For example, when we
have a
strong movement towards the masculine in our culture, we counteract it
with a
swing towards the feminine. In China, the
male saint Avalokiteshwara slowly evolved into Kuan Yin,
the female goddess of compassion! You can also see this in the
early
Christian adoption of Mary as a significant object of veneration.
Jung believed that, if we ignore the sexual opposite within us, we are
using only half of the potential available to us. In fact, the
balancing of male and
female qualities has been recognized for some time as beneficial to our
mental health - an issue thoroughly studied by Sandra Bem and others,
who
refer to the balance as androgeny
However interesting Jung's archetypes may be, they are based on
Jung's analysis of myth, literature, dreams, symbols, art, and so on.
It would be wise, I think, to look at instincts from a more scientific
perspective.
The scientific study of instincts really gets started in the 1930s,
with people such as the Dutch biologist Nikolaas Tinbergen and the
Austrian biologists Konrad Lorenz and Karl von Frisch, the three of
whom would go on to win a Nobel Prize together in 1973. We'll
begin with a wonderful example of instinctual behavior in
animals: The
three-spined stickleback is a one-inch long fish that one can find in
the
rivers and lakes of Europe. Springtime is, as you might expect,
the
mating
season for the mighty stickleback and the perfect time to see instincts
in action.
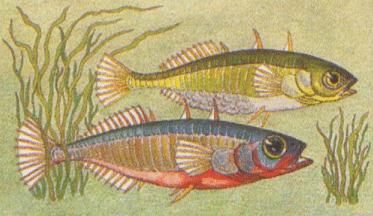
Certain changes occur in their appearances: The male, normally dull, becomes red above the midline. He stakes out a territory for himself, from which he will chase any similarly colored male, and builds a nest by depositing weeds in a small hollow and running through them repeatedly to make a tunnel. This is all quite built-in. Males raised all alone will do the same. We find, in fact, that the male stickleback will, in the mating season, attempt to chase anything red from his territory (including the reflection of a red truck on the aquarium's glass).
But that's not the instinct of the moment. The female undergoes a transformation as well: She, normally dull like the male, becomes bloated by her many eggs and takes on a certain silvery glow that apparently no male stickleback can resist. When he sees a female, he will swim towards her in a zigzag pattern. She will respond by swimming towards him with her head held high. He responds by dashing towards his nest and indicating it's entrance. She enters the nest, her head sticking out one end, her tail the other. He prods at the base of her tail with rhythmic thrusts. She releases her eggs and leaves the nest. He enters and fertilizes the eggs, and then, a thorough chauvinist, chases her away and waits for a new partner.
What you see working here is a series of sign stimuli and fixed actions: His zigzag dance is a response to her appearance and becomes a stimulus for her to follow, and so on. Perhaps I'm being perverse, but doesn't the stickleback's instinctive courtship remind you of some of our human courtship rituals? I'm not trying to say we are quite as mindless about it as the stickleback seems to be - just that some similar patterns may form a part of or basis for our more complex, learned behaviors.
Ethologists -- people who study animal behavior in natural settings - have been studying behaviors such as the sticklebacks' for over a century. Lorenz - one of the Nobel winners I mentioned earlier, developed an hydraulic model of how an instinct works: We have a certain amount of energy available for any specific instinctual system, as illustrated by a reservoir of water. There is a presumably neurological mechanism that allows the release of some or all of that energy in the presence of the appropriate sign stimulus: a faucet. There are further mechanisms -- neurological, motor, hormonal -- that translate the energy into specific fixed actions. Today, we might suggest that hydraulic energy is a poor metaphor and translate the whole system into an information processing one - each era has it's favorite metaphors. But the description still seems sound.
Every instinct in every animal is, of course, the result of eons of selection. One sociobiologist, David Barash, suggests a guiding question for understanding possible evolutionary roots of any behavior: "Why is sugar sweet”, that is, why do we find it attractive? One hypothesis is that our ancestors ate fruit to meet their nutritional needs. Fruit is most nutritious when it is ripe. When fruit is ripe, it is loaded with sugars. Any ancestor who had a taste for sugar would be a little more likely to eat ripe fruit. His or her resulting good health would make him or her stronger and more attractive to potential mates. He or she might leave more offspring who, inheriting this taste for ripe fruit, would be more likely to survive to reproductive age, etc. A more general form of the guiding question is to ask of any motivated behavior "How might that behavior have aided ancestral survival and/or reproduction?"
A curious point to make about the example used is that today we have refined sugar -- something which was not available to our ancestors, but which we discovered and passed on to our descendants through learned culture. It is clear that today a great attraction to sugar no longer serves our survival and reproduction. But culture moves much more quickly than evolution: It took millions of years to evolve our healthy taste for sugar; it took only thousands of years to undermine it.
SexIt is obvious
that we are attracted some people more than others.
Sociobiologists
have the same explanation for this as for everything else, based on the
archetypal question "why is sugar sweet?" So why is sex "sweet"?
We should be sexually
attracted
to others whose characteristics would maximize our genetic success,
that
is, would give us many healthy, long-lived, fertile children.
We should find healthiness attractive and, conversely, illness unattractive. We should find "perfect" features attractive, and deformities unattractive. We should find vitality, strength, vigor attractive. We should find "averageness" attractive -- not too short, not too tall, not too fat, not too thin.... Quasimodo, for all his decency, had a hard time getting dates.
These differences between the sexes is known as sexual dimorphism, and the process that leads to these differences is called sexual selection. Small functional differences between the sexes can become large nonfunctional ones over many generations. If female birds are instinctively inclined to prefer colorful males -- perhaps because colorful males have served to distract predators from ancestral females and their chicks -- then a male that is more colorful will have a better chance, and the female with a more intense attraction to color a better chance, and their offspring will inherit their colors and intense attraction to colors and so on and so on... until you reach a point where the colors and the attraction are no longer a plus, but become a minus, such as in the birds of paradise. Some males cannot even fly under the weight of all their plumage.
Human beings are only modestly dimorphic. But boy are we
aware
of the dimorphisms! Women tend to find tall, well-muscled men
more attractive, for example. Men tend to like youth and nicely rounded
softness attractive. An interesting odd detail comes to mind
here: Youth and "nicely rounded softness" are slightly contradictory,
since the young woman tends to be slender and "boyish", while the
mature woman tends to develop a more "motherly" figure. Perhaps this
plays a part in the cycles of women's fashion: One decade, women try to
achieve rail thinness; the next they work on exaggerating their breasts
or hips. In today's bizarre world of plastic surgery, we see thin women
with disproportionately large breasts! Another odd detail is
that, while women like a strong man, few are attracted to the
overly-muscled body-builder types. The sociobiological explanation is a
logical one: Too much of a good thing is a deviation from
averageness, and a signal of mutation.
The dimorphism is also found in our behaviors. David Barash puts it so: "Males tend to be selected for salesmanship; females for sales resistance." Females have a great deal invested in any act of copulation: the limited number of offspring she can carry, the dangers of pregnancy and childbirth, the increased nutritional requirements, the danger from predators...all serve to make the choice of a mate an important consideration. Males, on the other hand, can and do walk away from the consequences of copulation. Note, for example, the tendency of male frogs to try to mate with wading boots: As long as some sperm gets to where it should, the male is doing alright.
So females tend to more fussy about who they have relations with. They are more sensitive to indications that a particular male will contribute to their genetic survival. One of the most obvious examples is the attention many female animals pay to the size and strength of males, and the development of specialized contests, such as those of deer and sheep, to demonstrate that strength.
There are less obvious things as well. In some animals,
males
have to show, not just strength, but the ability to provide. This
is especially true in any species which has the male providing for the
female during her pregnancy and lactation -- like humans!
Sociobiologists
suggest that, while men find youth and physical form most attractive,
women
tend to look for indications of success, solvency, savoir-faire.
Further, they suggest, women may find themselves more interested in the "mature" man, as he is more likely to have proven himself, and less interested in the "immature" man, who presents a certain risk. And women should be more likely to put up with polygyny (i.e. other wives) than men with polyandry (other husbands): Sharing a clearly successful man is better in come cases than having a failure all to yourself. And, lo and behold, polygyny is even more common than monogamy, while polyandry is found in perhaps two cultures (one in the Himalayas and the other in Africa), and in both it involves brothers "sharing" a wife in order not to break-up tiny inherited properties..
Taking it from the other direction, males will tolerate less infidelity than females: Females "know" their children are theirs; males never know for sure. It could always be the plumber's kid! Genetically, it matters less if males "sow wild oats" or have many mates or are unfaithful. And, sure enough, most cultures are harder on women than men when it comes to adultery. In most cultures, in fact, it is the woman who moves into the husband's family (virilocality) -- as if to keep track of her comings and goings.
From our culture's romantic view of love and marriage, it is interesting to note that in most cultures a failure to consummate a marriage is grounds for divorce or annulment. In our own culture, infertility and impotence are frequent causes of divorce. It seems reproduction is more important than we like to admit.
Of course, there is a limit to the extent to which we
generalize
from
animals to humans (or from any species to any other), and this is
especially
true regarding sex. We are very sexy animals: Most animals
restrict their sexual activity to narrowly defined periods of time,
while
we have sex all month and all year round. We can only guess how
we
got to be this way. Perhaps it has to do with the long-term
helplessness
of our infants. What better way to keep a family together than to
make it so very reinforcing!
A part of our personality is the role of male or female we
must play.
For
most people that role is determined by their physical gender. But
Freud, Jung, and Adler, as well as more recent theorists, feel that we
are all really bisexual
in
nature. When we begin our lives as fetuses, we have undifferentiated
sex
organs that only gradually, under the influence of hormones, become
male
or female. Likewise, when we begin our social lives as infants, we are
neither male nor female in the social sense. Almost immediately -- as
soon
as those pink or blue booties go on -- we come under the influence of
society,
which gradually molds us into men and women.
Since most of us feel pretty solidly heterosexual, this idea that we
are all bisexual underneath it all isn't always cheerfully accepted.
But it is quite clear that people are extremely "flexible" when it
comes to sex. We quickly develop all sorts of odd habits and interests
that have little to do with reproduction at all! Freud suggested that
children are "polymorphously perverse", but that quality applies much
better to adults.
This idea has been recently reinforced by our increased knowledge of
the life of our closest genetic relative, the bonobo chimpanzee.
The bonobo uses sex for far more than reproduction. It has become
a way of establishing social relationships. They have sex with
old lovers and new acquaintances. They have sex with the old and
the young. They have heterosexual sex and homosexual sex.
They even have certain varieties of incestuous sex! What a
species of sex fiends, you say? Take a look at us!

Human beings, of course, have developed all kinds of rules about
sex. We have strong taboos about incest. Many societies
have strict rules about homosexuality. Many have rules about
promiscuity. We even have rules about what parts of the body may
be exposed and which not, and which may be ridiculously exaggerated
(such as penis cones among certain New Guinea tribesmen, and brassieres
that push 'em up and out!). Some societies even force women to
cover
themselves from head to toe, so as to keep men's sexual arousal to a
minimum (as if that's ever going to happen). But the point is
that, despite all these rules, and the punishments that come with
disobedience, people continue to do odd things with their genitalia.
Children
And then we have the children. We are attracted to them, and they are attracted to us. Adults of many species, including ours, seem to find small representatives of their species, with short arms and legs, large heads, flat faces, and big, round eyes... "cute" somehow -- "sweet," the sociobiologist might point out. It does make considerable evolutionary sense that, in animals with relatively helpless young, the adults should be attracted to their infants. It may also explain our affection for puppies, kitties, teddy bears, and baby dolls.
The infants, in turn, seem to be attracted to certain things as well. Goslings, as everyone knows, become attached to the first large moving object they come across in the first two days of life -- usually mother goose (occasionally Konrad Lorenz or other ethologists). This is called imprinting. Human infants respond to pairs of eyes, female voices, and touch.
The goslings respond to their sign-stimulus with the following response, literally following that large moving object. Human infants, of course, are incapable of following, so they resort to subterfuge: the broad, full bodied, toothless smile which parents find overwhelmingly attractive.
Sociobiologists go on to predict that mothers will care for
their
children
more than fathers (they have more invested in them, and are more
certain
of their maternity); that older mothers will care more than younger
mothers
(they have fewer chances of further procreation); that we will be more
solicitous of our children when we have few (or only one!) than when we
have many; that we will increase our concern for our children as they
get
older (they have demonstrated their survival potential); and that we
will
tend to push our children into marriage and children of their own.
Separation anxiety is a very common problem among children, especially younger ones. It is found in about 4% of kids. The problem is excessive anxiety about separation from the child's parents, other family members, or even their home. When separated, they become withdrawn and depressed and may have difficulty concentrating. They often develop other fears, anxiety about death, and nightmares. Of course, some separation anxiety is a normal part of childhood, so this can be a bit of a subjective call.
Separation anxiety usually occurs in tight, loving families. It often begins with some kind of life stress, such as moving to a new home or town, starting at a new school, or the death of a pet or relative. fortunately, for most children, it ends sometime in adolescence if not earlier.Helping behavior is likely when it involves our children, parents, spouses, or other close relations. It is less and less likely when it involves cousins or unrelated neighbors. It is so unusual when it involves strangers or distant people of other cultures and races that we recall one story -- the good Samaritan -- nearly 2000 years after the fact.
Sociobiologists predict that helping decreases with kinship distance. In fact, it should occur only when the sacrifice you make is outweighed by the advantage that sacrifice provides the genes you share with those relations. The geneticist J. B. S. Haldane supposedly once put it this way: "I'd gladly give my life for three of my brothers, five of my nephews, nine of my cousins...." Since my brothers and I share 50% of our genes, it would take three of them (150%) to beat saving my own butt (100%), and so on. This is called kin selection. Altruism based on genetic selfishness, at least according to Haldane!
Another kind of altruistic behavior is herd behavior. Some animals just seem to want to be close, and in dangerous times closer still. It makes sense: By collecting in a herd, you are less likely to be attacked by a predator. Other animals will signal the entire herd when they spot a predator. One famous example is the springbok of South Africa, which jumps straight up in the air when it sees a lion. Another is the prairy dog, which barks when it sees a coyote. Of course, that draws the attention of the predator to the one who is giving the signal, which is dangerous for that particular individual. But the next time, it will be some other member of the herd. It's a trade-off. Animals often help any member of their group, with the instinctual "understanding" that they may be the beneficiaries the next time they need help themselves.
Robert Trivers has suggested that some animals (ourselves included) engage in a more sophisticated version of helping called reciprocal altruism. Here you would be willing to help someone else if it is understood that he or she will do the same for you, or reciprocate in some other way, "tit for tat." Clearly, it helps if you have the ability to recognize individuals and to recall debts!
Other geneticists have pointed out that, if there is a genetic basis for reciprocal altruism, there will also be some individuals that cheat by allowing others to do for them without ever meeting their own obligations. In fact, depending on the advantages that reciprocal altruism provides and the tendency of altruists to get back at cheaters, cheaters will be found in any population. Other studies have shown that "sociopathy," guiltless ignoring of social norms, is found in a sizable portion of the human population.
There is, of course, no need for a human being to be 100% altruist or 100% cheat. Most of us (or is it all of us?), although we get angry at cheats, are quite capable of cheating when the occasion arises. We feel guilt, of course, be we can cheat. A large portion of the human psyche seems to be devoted to calculating our chances of success or failure at such shady maneuvers.
Aggression
Next to sex, personality theorists of the past have used aggression to explain human behavior most. Alfred Adler was one of the first: While he was Freud's favorite at first, he repeatedly annoyed the master by introducing the idea that sex drive wasn't the only thing that could lead to psychological problems: So could the aggression drive! Like many concepts in psychology, aggression has many definitions, even many evaluations. Some think of aggression as a great virtue (e.g. "the aggressive businessperson"), while others see aggression as symptomatic of mental illness.
The fact they we do keep the same word anyway suggests that there is a commonality: Both positive and negative aggression serve to enhance the self. The positive version, which we could call assertiveness, is acting in a way that enhances the self, without the implication that we are hurting someone else. The negative version, which we might call violence, focuses more on the "disenhancement" of others as a means to the same end.
Although the life of animals often seems rather bloody, we must take care not to confuse predation -- the hunting and killing of other animals for food -- with aggression. Predation in carnivorous species has more in common with grazing in vegetarian species than with aggression between members of the same species. Take a good look at your neighborhood cat hunting a mouse: He is cool, composed, not hot and crazed. In human terms, there is not the usual emotional correlate of aggression: anger. He is simply taking care of business.
That distinction noted, there remains remarkably little aggression in the animal world. But it does remain. We find it most often in circumstances of competition over a resource. This resource must be important for "fitness," that is, relevant to one's individual or reproductive success. Further, it must be restricted in abundance: Animals do not, for example, compete for air, but may for water, food, nesting areas, and mates.
It is the last item -- mates -- that accounts for most
aggression in
mammals. And it is males that are most noted for this aggression. The
connection between masculinity and aggression is so strong, Adler once
used the phrase "masculine protest" to refer to the aggressive
instinct. Yes, Virginia, there are differences between the sexes: Both
libido (sex drive) and aggression are greater (on average!) in the
human male. And, naturally, libido and aggression are
interrelated!
As we mentioned earlier, females have so much at stake in any act of copulation -- so many months gestation, the increased energy requirement, susceptibility to attack, the dangers of birth, the responsibility of lactation -- that it serves their fitness to be "picky" when looking for a partner. If females are picky, males must be show-offs: The male must demonstrate that he has the qualities that serve the female's fitness, in order to serve his own fitness. Deer and other antlered and horned mammals are good examples. Mind you, this need not be conscious or learned; in all likelihood, it is all quite instinctual in most mammals. It may possibly have some instinctual bases in us as well.
Some of this aggressiveness may in fact be mediated by testosterone, the "male" hormone. Inject testosterone into female mice and their threshold for aggressive behavior goes down. Remove testosterone from male mice (by castrating the poor things) and their thresholds go up. But I must add that testosterone does not cause aggression, it just lowers the threshold for it.
But females in many species can be quite aggressive (such as female guinea pigs), and females in most species can be extremely aggressive in certain circumstances (such as when facing a threat to her infants). In human societies, the sociological statistics are clear: Most violent crime is committed by men. But we have already noticed that, as women assert their rights to full participation in the social and economic world, those statistics are changing. Time will tell the degree to which testosterone is responsible for aggression in people.
Nevertheless, males engage in a great deal of head-butting. But one can't help but notice that these contests "over" females seldom end in death or even serious injury in most species. That is because these contests are just that: contests. They are a matter of displays of virtues, and they usually include actions that serve as sign stimuli to the opponent that the contest has ended in his favor: surrender signals. Continued aggression is of little advantage to either the loser or the winner. Even male rattlesnakes don't bite each other!
Territoriality and dominance hierarchies -- once thought to be
major
focuses of aggressive behavior -- seem to be relatively less
significant.
Animals tend to respect territorial and status claims more than dispute
them. It is only when circumstances, whether natural or humanly
created,
are out of the ordinary that we see much aggression. And low food
supplies
likely have little to do with aggression. Southwick,
studying Rhesus
monkeys
in the London Zoo, found that reducing the food supplies by 25% had no
effect on the amount of aggression found, and reducing the food
supplies
by 50% actually decreased aggression! We find the same thing among
primitive
people.

So why so much aggression in people? One possibility is our lack of biological restraints. Sociobiologists predict that animals that are poorly equipt for aggression are unlikely to have developed surrender signals. Man, they say, is one of these creatures. But we developed technology, including a technology of destruction, and this technology "evolved" much too quickly for our biological evolution to provide us with compensating restraints on aggression. Experience tells us that guns are more dangerous than knives, though both are efficient killing machines, because a gun is faster and provides us with less time to consider our act rationally -- the only restraint left us.
Another problem is that we humans live not just in the "real" world, but in a symbolic world as well. A lion gets aggressive about something here-and-now. People get aggressive about things that happened long ago, things that they think will happen some day in the future, or things that they've been told is happening. Likewise, a lion gets angry about pretty physical things. Calling him a name won't bother him a bit.
A lion gets angry about something that happens to him personally. We get angry about things that happen to our cars, our houses, our communities, our nations, our religious establishments, and so on. We have extended our "ego's" way beyond our selves and our loved ones to all sorts of symbolic things. The response to flag burning is only the latest example.
If aggression has an instinctual basis in human beings, we would expect there to be a sign stimulus. It would certainly not be something as simple as bright red males during mating season, as in stickleback fish. If we go back to the idea of competition as a fertile ground for aggression, we notice that frustration is a likely candidate. There are two of you who want the same thing; if one grabs it, the other doesn't get it and is unhappy; so he takes it, and now the other is unhappy; and so on. Goal-directed behavior has been blocked, and that is frustration.
Variations on that theme abound: We can be frustrated when an on-going behavior is interrupted (trying tripping someone); we can be frustrated by a delay of goal achievement (cut in front of someone on line at the movie theater); or we can be frustrated by the disruption of ordinary behavior patterns (try stealing my morning coffee). We are flexible creatures.
But we must beware here: Other things can lead to aggression
besides
frustration (or aren't highly paid boxers engaged in aggression?) and
frustration
can lead to other things besides aggression (or doesn't social
impotence
lead to depression?). Further, as Fromm points out, frustration (and
aggression)
is in the eyes of the beholder. He feels that the frustration must be
experienced
as unjust or as a sign of rejection for it to lead to aggression.
Many psychologists, sociologist, anthropologists, and others are wary of the explanations - convincing though they sometimes are - of the sociobiologists: For every sociobiological explanation, we can find a cultural explanation as well. After all, culture operates by the same principles as evolution.
There are many different ways to do any one task, but in the context of a certain physical environment and a certain culture, some ways of doing things work better than others. These are more likely to be "passed on" from one generation to the next, this time by learning.
Now, cultures need to accomplish certain things if they are to survive at all. They must assure effective use of natural resources, for example, which might involve the learning of all sorts of territorial and aggressive behaviors, just like in sociobiological explanations. And they must assure a degree of cooperation, which might involve learning altruistic behaviors, rules for sharing resources and for other social relationships, just like the ones in sociobiological explanations. And they must assure a continuation of the population, which might involve certain courtship and marital arrangements, nurturant behaviors, and so on, just like in sociobiological explanations.
If a society is to survive - and any existing society has at least survived until now - it must take care of the very same issues that genetics must take care of. And, because learning is considerably more flexible than evolutionary adaptation, we would expect culture to tend to replace genetics. That is, after all, only evolutionary good sense!
So do we have instincts? If we define instincts as automatic reflex-like connections - no, probably not. But define instincts as "strong innate tendencies toward certain behaviors in certain situations" - yes, we probably do. The important point is that we (unlike animals) can always say no to our instinctual behaviors, just like we can say no to our learned ones!