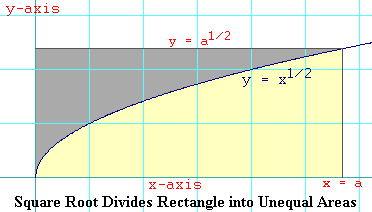
The figure shows the square root function with the rectangle drawn and the two unequal areas shaded. The area we are interested in finding is shaded in yellow. The area that constitutes the rest of the rectangle is shaded gray. We already know that the Rieman sum method will not help us much in evaluating the yellow area because we end up with a summation that we don't know how to do. But the total area of the rectangle is clear. We know its base and its height, so when we take their product we get:
_
Arectangle = a Öa = a(a1/2) = a3/2
We also know that the sum of the gray and yellow areas has to equal the total
area of the rectangle:
Arectangle = a3/2 = Agray + Ayellow Ayellow = a3/2 - Agray
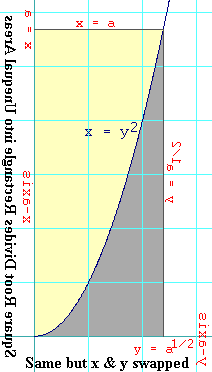 So if we can find the gray area, we can solve this problem. Do you see
anything familiar about the gray area? Perhaps if we rotate and flip the
diagram you'll see it.
The second diagram shows how rotating and flipping the drawing has the
effect of swapping the x and y axis.
Do you remember the trick from algebra for finding the graph of
the inverse function? This was where you rotated the paper ninety
degrees and then viewed it from the back. The writing appeared backwards,
but the graph that you saw was that of the inverse function. By rotating
and flipping the graph of the square root function, we see its inverse,
which is the square function.
So if we can find the gray area, we can solve this problem. Do you see
anything familiar about the gray area? Perhaps if we rotate and flip the
diagram you'll see it.
The second diagram shows how rotating and flipping the drawing has the
effect of swapping the x and y axis.
Do you remember the trick from algebra for finding the graph of
the inverse function? This was where you rotated the paper ninety
degrees and then viewed it from the back. The writing appeared backwards,
but the graph that you saw was that of the inverse function. By rotating
and flipping the graph of the square root function, we see its inverse,
which is the square function.
Now finding the
gray area looks a whole lot like finding the area under the
Agray = ((a1/2)3)/3 = (a3/2)/3And to find the yellow area, we simply go back to the previous equation:
Ayellow = a3/2 - Agray = a3/2 - (a3/2)/3 = (2/3)a3/2and that is the solution.
email me at hahn@netsrq.com